
Mongoose
Urva auropunctata
Report if seen anywhere on Maui
Known from and potential habitat
Species Info General
In Hawai‘i, you might see a mongoose darting across the highway, or worse, breaking into your chicken coop. Native to India, these small, carnivorous mammals look similar to weasels. Widespread on Hawai‘i Island, Maui, Molokai, and O‘ahu, mongoose are present in a range of habitats, from rainforests to dryland areas. Mongoose are opportunistic and will feed on birds, eggs, small mammals, reptiles, insects, and fruit. They have severely impacted native wildlife populations of birds and sea turtles by feeding on their eggs and hatchlings.
While not a MISC target pest, mongoose are Hawai‘i Injurious Wildlife. It is illegal to introduce, transport, keep, or breed mongoose without a permit from the HDOA. Mongoose may be widespread on Maui but they are not present on Lāna‘i or Kaua‘i. If you see a mongoose on these islands, report to 643PEST.org. It is not necessary to report sightings on Maui, Molokai, O‘ahu, or Hawai’i Island. Small animal traps can be used for control.
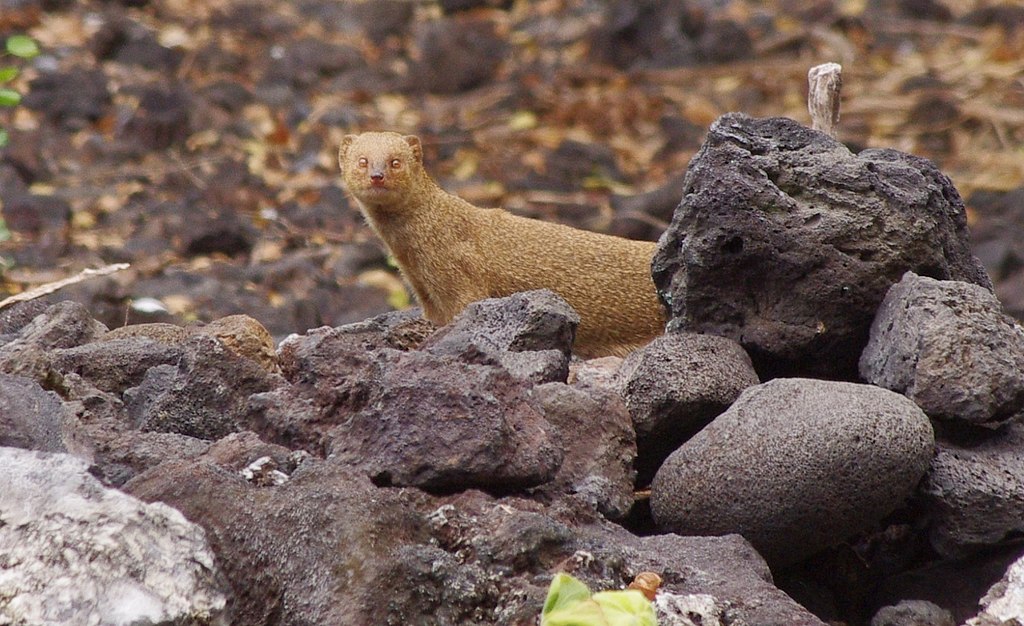
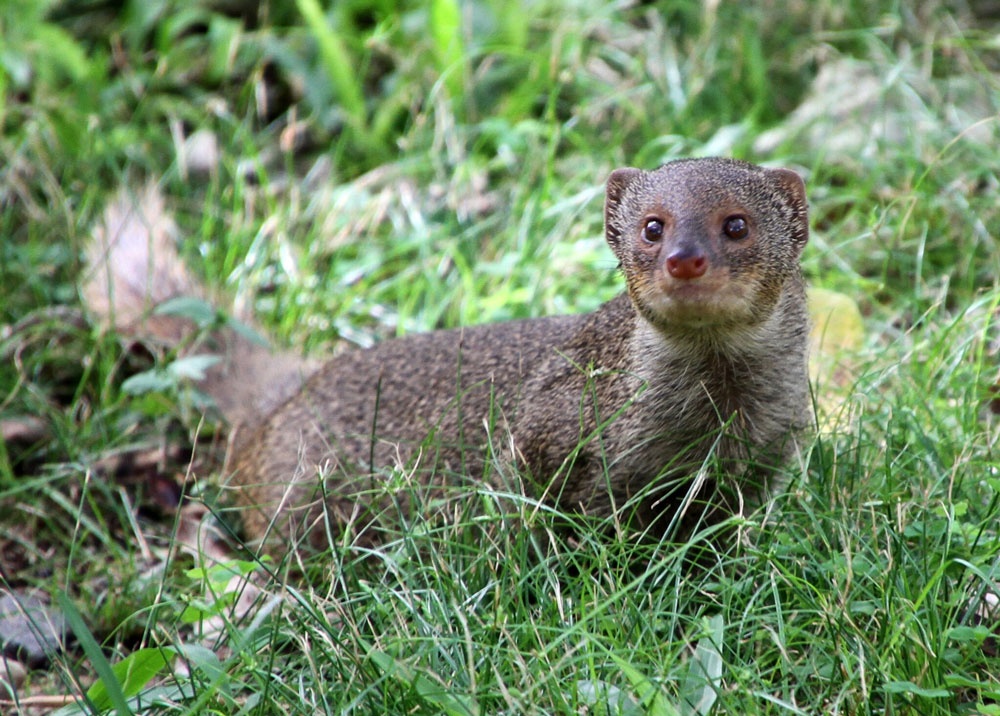
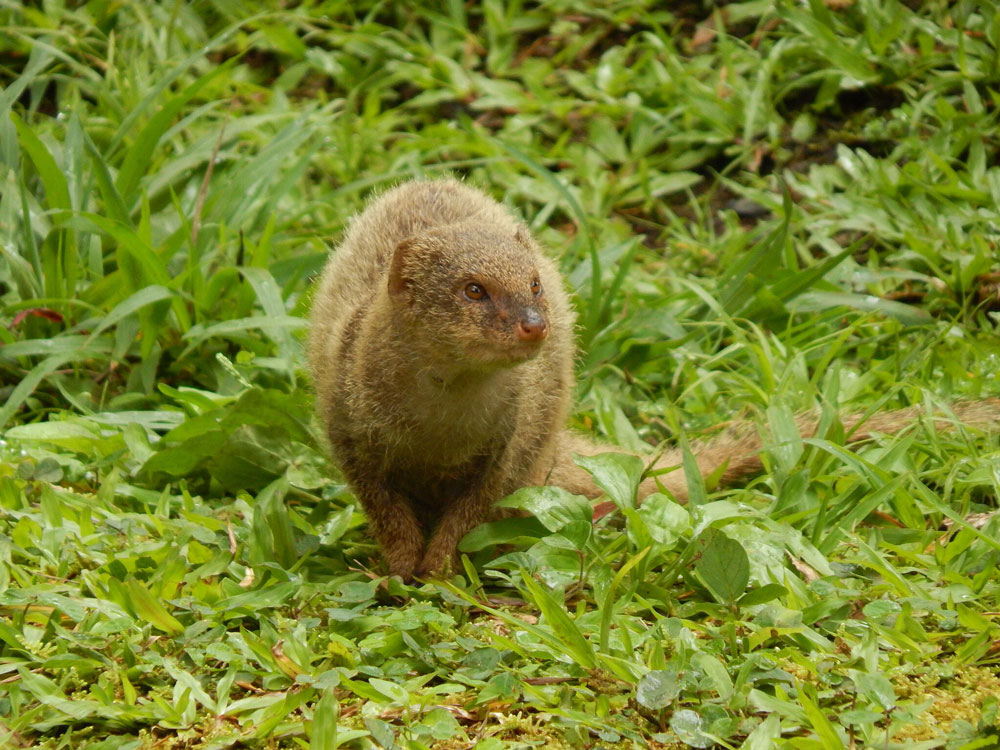



Identification/Description
Mongoose have long bodies, short legs, and a tail as long as its body. They can grow up to 26 inches. Mongoose are light brown in color, with rounded ears and a pointed nose. They are usually active during the day and sleep in dens at night.
Impacts
- Mongoose prey on eggs and hatchlings of birds and endangered sea turtles.
- They have contributed to the extinction of ground-nesting birds in Jamaica and Fiji. Commonly kills birds, including federally listed endangered Hawaiian birds.
- Can cause damage to gardens and agriculture; may prey on chickens and other poultry.
- Carries diseases like leptospirosis and murine typhus. Murine typhus can be transmitted to humans when they are bitten by a flea that has fed on an infected animal.
On Maui
Mongoose were introduced to Maui in 1883 by the sugar industry to control rats in the sugar fields. This was a misguided attempt. While rats are part of a mongoose’s diet, their impacts on native wildlife outweighs their effect on rat populations.
Mongoose are not an example of biological control. Private individuals introduced the mongoose without any research to determine impact on native species.
Control info/Info on what MISC does about it
- Coming Soon!
